| Methods | Description |
| Agitated Saline Study with Transthoracic Echocardiogram | Transthoracic echocardiography-guided pericardiocentesis has been performed since 1979.Once the sheath is inserted into the pericardial space, sheath position may be verified by instillation of 5 to 8 mL of agitated saline. Transthoracic echocardiogram can then be used to visualize the saline bubbles in the pericardial space. Example of agitated saline study: |
| Fluoroscopy | During pericardiocentesis, a 0.035-inch guidewire is typically inserted into pericardial space under fluoroscopic guidance. The wire follows the path of outer cardiac border and crosses the midline. Example of fluoroscopic guided wire placement: 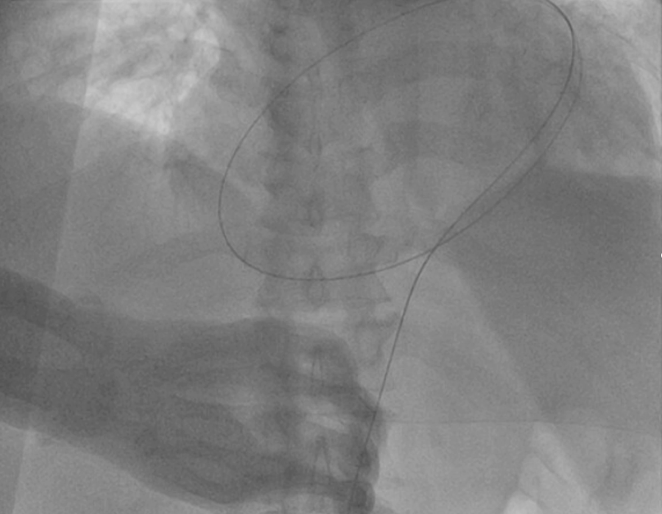 |
| Pressure Characteristics | Pressure waveform can help confirm correct placement in pericardial space. Pericardial tracing has a more sinusoidal waveform, which is minimally fluctuating. Right ventricular pressure waveforms have clear systolic and diastolic phases with higher peak pressures during systole and are pulsatile. Example of pericardial wave form: 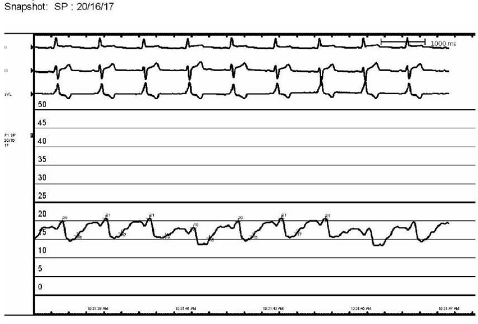 |
| Contrast | Contrast medium may be injected to confirm opacification of the pericardial space under fluoroscopy. |
| Oxygen Saturation Measurement | Oxygen saturation of the pericardial fluid should be close to 0% in comparison to oxygen saturation of the right ventricle between 60-70%. |
| Aspirate Analysis | Fluid aspirated from the pericardial space can be analyzed for hematocrit levels. Pericardial fluid typically has a low hematocrit level compared to blood. Hematocrit of serosanguinous fluid should be 2-5%, in comparison to hematocrit from intracardiac or intravascular source of around 35%. Sanguinous pericardial effusions typically have a moderate hematocrit level of 5-10%, and usually less than 50% of the patient’s peripheral blood hematocrit. |
| Clotting Test | Place a small amount of pericardial fluid in an equipment tray. Blood or bloody fluid from the pericardial space generally does not clot. This is because pericardial effusion often accumulates over time, and the clotting factors within the fluid degrade. Blood aspirated directly from the right ventricle will generally clot quickly because it is fresh, and the clotting factors are intact. |